Laser Engraving vs CNC Engraving for Glass Guide
The laser engraving vs CNC engraving for glass comparison is a crucial analysis for any modern glass fabrication workshop. These two powerful technologies both create stunning designs on glass, but they do so through fundamentally different methods, resulting in distinct visual and tactile qualities. Laser engraving is a non-contact, thermal process that creates a frosted, surface-level mark.1 CNC engraving is a contact-based, mechanical process that carves a deep, brilliant groove into the glass. This guide provides a definitive comparison. It details the mechanics, applications, and strategic advantages of each method to help you make an informed decision for your specific needs.
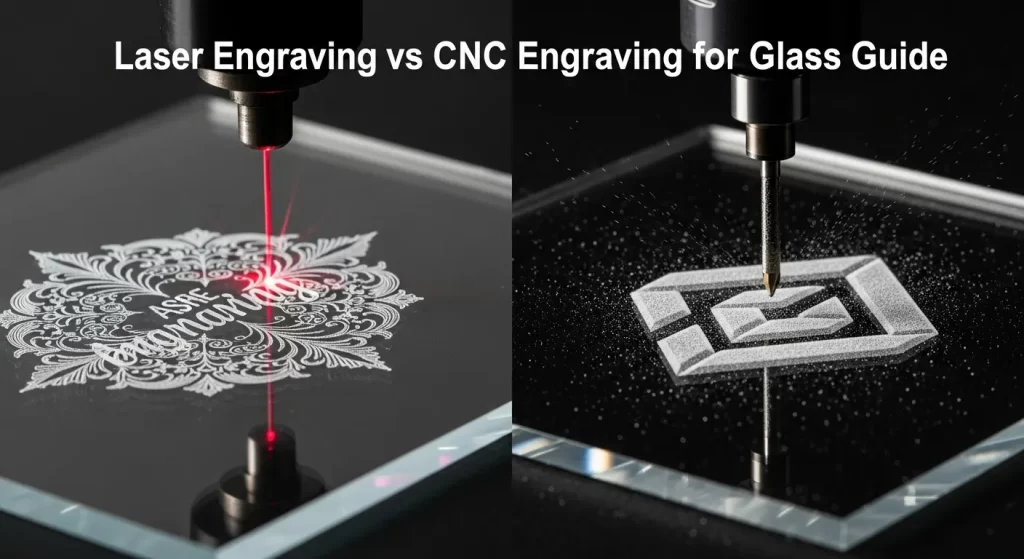
What is the Core Difference in Laser vs CNC Engraving for Glass?
The core difference is that laser engraving is a non-contact, thermal process, while CNC engraving is a contact-based, mechanical process.2 A laser uses a focused beam of light to create micro-fractures in the glass, resulting in a frosted mark.3 A CNC machine uses a physical, rotating diamond-tipped tool to physically carve away the glass, creating a deep and brilliant groove.4
This fundamental distinction in the method—heat versus physical force—is what dictates every other difference between the two technologies. It influences the final appearance, the depth of the mark, the types of designs each is best suited for, and the overall workflow. Understanding this core principle of thermal versus mechanical is the first step in mastering these advanced decorative techniques.
How Does Laser Engraving for Glass Work?
Laser engraving for glass is a high-precision, non-contact process that uses a focused beam of laser light to create a mark on the glass surface.5 The intense energy of the laser is absorbed by the glass, causing rapid, localized heating.6 This thermal stress induces tiny micro-fractures within the glass.7 The collection of millions of these microscopic fractures creates the final, visible engraved image.
What is the Role of Thermal Stress in Laser Engraving?
Thermal stress is the primary mechanism behind laser engraving on glass. Glass is a poor thermal conductor. This means that when the laser strikes the surface, the heat does not dissipate quickly. Instead, it becomes highly concentrated in a very small area. This intense, localized heat causes the glass in that spot to expand rapidly. The surrounding cool glass resists this expansion. This conflict creates a significant amount of stress, which is relieved by the formation of a controlled micro-fracture. The laser moves at incredibly high speeds, creating thousands of these fractures per second to form the design.
What is the Appearance of a Laser-Engraved Finish?
The appearance of a laser-engraved finish is typically a clean, bright, frosted white mark. It has a very fine, almost sandy texture. Because the process is controlled by a computer, the level of detail can be exceptionally high. This allows for the reproduction of complex patterns and even photorealistic images. The mark is on the surface of the glass and has very little depth. It does not sparkle. Instead, it creates a soft, elegant contrast against the clear glass. This is the core technology explored in our guide where glass laser etching technology is explained.
How Does CNC Engraving for Glass Work?
CNC engraving for glass is a physical, subtractive process that uses a computer-controlled machine to carve a design directly into the glass.8 The machine uses a high-speed rotating spindle that holds a specialized, diamond-tipped cutting tool, often called a burr. The diamond tool is physically pressed into the glass and moved along a programmed path. This carves away the material, creating a distinct groove with significant depth.
What is the Role of the Diamond Rotary Tool?
The diamond rotary tool is the cutting instrument of the CNC machine. These tools are made by bonding fine industrial diamond particles to a metal shank. Diamond is the only material hard enough to effectively cut glass in this manner. The tool spins at thousands of RPM. As the CNC machine moves it across the glass, the diamond particles abrade and chip away the glass material in a very controlled way. The shape of the tool's tip, such as a V-shape or a ball-nose, determines the profile of the engraved groove. This mechanical action is the defining feature of the process.
What is the Appearance of a CNC-Engraved Finish?
The appearance of a CNC-engraved finish is defined by its depth, clarity, and brilliance. Unlike the frosted mark of a laser, a CNC engraving is a true, V-shaped or U-shaped groove carved into the glass. This physical depth gives the design a tangible, three-dimensional quality. The sharp, angled facets of the cut groove catch and refract light. This creates a brilliant, sparkling, jewel-like effect. This is the classic look of traditional engraved glass. It is a bold, high-impact finish that is valued for its perceived quality and substance.
Head-to-Head Comparison: Laser vs CNC Engraving
The choice between laser and CNC engraving depends entirely on the desired outcome. One is a tool of subtle precision; the other is a tool of brilliant depth. This table provides a direct comparison of their key attributes to help clarify the laser engraving vs CNC engraving for glass decision.
| Feature | Laser Engraving | CNC Engraving |
| Method | Non-contact, thermal (heat stress). | Contact-based, mechanical (cutting). |
| Final Finish | Frosted, matte, white appearance. | Clear, brilliant, sparkling V-groove. |
| Depth | Very shallow, surface-level effect. | Significant, controllable depth. |
| Tactile Feel | A slightly rough, sandy texture. | A distinct, deep groove can be felt. |
| Primary Tool | Focused beam of laser light. | Rotating diamond-tipped burr. |
| Coolant Required | No (Air assist for debris removal). | Yes (Mandatory to prevent thermal shock). |
| Level of Detail | Excellent for photorealistic raster images. | Excellent for sharp, clean vector lines and text. |
| 3D Capability | Can do sub-surface 3D engraving. | Can do 3D surface carving (V-carve). |
Which Method Offers Superior Precision and Detail?
The answer to which method offers superior precision depends on the type of design being created. For photorealistic images or complex, grayscale raster graphics, laser engraving is superior. For sharp, clean, and deep vector lines, such as in text or logos, CNC engraving often produces a crisper and more brilliant result.
A laser engraver works much like a printer. It can scan back and forth, creating an image from thousands of fine dots. This allows it to reproduce the subtle tones and gradients of a photograph with incredible detail. A CNC machine, on the other hand, excels at following a vector path. It can create a perfectly smooth, continuous line with a sharp, beveled edge that a laser cannot replicate. The top glass engraving software tools are often specialized for one of these two types of workflow.
How Do the Depth and Tactile Feel Compare?
The depth and tactile feel of the two methods are dramatically different. CNC engraving creates a true, deep groove in the glass that can be easily felt. Laser engraving creates a surface-level texture that is only slightly rough to the touch.9 This difference in dimensionality is a key factor in their respective applications.
The depth of a CNC engraving is controllable. An operator can program the machine to make multiple passes. This can create a V-groove that is several millimeters deep. This physical depth is what gives the design its brilliant, light-refracting quality. Laser engraving, by its nature, creates a very shallow effect. The micro-fractures penetrate only a fraction of a millimeter into the surface. The result is visually striking but lacks the physical substance of a CNC engraving.
What Are the Key Differences in Speed and Efficiency?
The speed and efficiency of each process are highly dependent on the type and complexity of the job. For large, filled raster images, a laser is generally much faster. For simple, deep vector line work, a CNC machine can be more efficient. The overall workflow and setup time also play a significant role in the total efficiency.
How Does Job Type Affect Engraving Speed?
The type of job has a major impact on speed.
- Raster Engraving (Images): For engraving a large, solid black square or a photograph, a laser is much faster. Its head can move at high speeds, scanning back and forth to quickly cover the area. A CNC machine would have to clear out this same area with a small tool, which is a much slower process.
- Vector Engraving (Lines/Text): For engraving the outline of a square or a line of text, a CNC machine can be very fast. It can simply trace the vector path at a high feed rate. A laser, when used in "vector cutting" mode on glass, is often run at a slower speed to create a clean mark.
What is the Impact of Setup Time?
The setup time for a laser is generally faster. The operator simply needs to place the glass in the machine, set the focus of the laser, and load the program. The setup for a CNC machine is more involved. The operator must securely clamp the glass, install the correct diamond tool, calibrate the tool's length, and set up the coolant system. While the CNC setup takes longer, its ability to create deep, brilliant results often justifies the extra time for high-value jobs.
When is Laser Engraving the Best Choice for Glass?
Laser engraving is the best choice when the design requires extremely fine detail, grayscale shading, or when a non-contact process is essential.10 It is the ideal technology for applications where a subtle, elegant, frosted mark is desired. The market for personalized goods has been greatly expanded by the accessibility of laser technology.
Laser engraving is the clear winner for:
- Photorealistic Images on Glass: Its ability to reproduce photographs is unmatched.
- Intricate Logos with Fine Details: For complex logos with very small elements.
- Surface Marking and Serialization: For adding small part numbers, QR codes, or barcodes.
- Awards with a Lot of Small Text: It can produce very small, readable text clearly.The entire process is a key part of modern decorative techniques.
When is CNC Engraving the Superior Option for Glass?
CNC engraving is the superior option when the design calls for depth, brilliance, and a bold, tactile feel. It is the technology of choice for creating high-end, premium decorative pieces where a sense of substance and quality is paramount. It is the modern evolution of the traditional craft of hand engraving.
CNC engraving is the superior choice for:
- High-End Corporate and Sporting Awards: The deep, V-carved text and logos have a prestigious, high-value appearance.
- Architectural Glass and Signage: Deep-carved logos and text in a corporate lobby are highly visible and durable.12 This is a key application in glass engraving for decor and branding.
- Personalized Gifts with a "Carved" Look: For a bold monogram on a decanter or a deep-cut design on a vase.
- Creating a True V-Groove: This classic beveled letterform can only be achieved with a physical cutting tool.
What About Advanced 3D Engraving Capabilities?
The term "3D engraving" can refer to two very different advanced techniques, one exclusive to lasers and the other to CNC machines. This is where the technologies diverge into truly unique capabilities. These advanced methods are at the forefront of engraving and etching innovations.
How Does 3D Sub-Surface Laser Engraving Work?
3D sub-surface laser engraving is a remarkable process that is only possible with a specialized laser. The laser beam is focused at a precise point inside a solid block of optical crystal. This creates a tiny, contained fracture. By plotting millions of these points, the machine can build a complex, three-dimensional model that appears to float inside the glass. This technology is explained in depth in our guide on how 3D glass engraving machines work. It has a wide range of uses in the world of 3D glass art machine applications.
Can a CNC Machine Create a 3D Effect?
Yes, a CNC machine can create a powerful 3D effect on the surface of the glass using a technique called V-carving. By using a V-shaped tool and specialized software, the machine can vary the depth of the cut as it moves. In wider areas of a design, the tool goes deeper, creating a wider, beveled line. In narrower areas, the tool rises, creating a thinner line. This creates a fascinating illusion of depth and dimension on a 2D surface.
What Are the Safety and Maintenance Considerations?
Both technologies have their own specific safety protocols and maintenance requirements. A professional workshop must be well-versed in the procedures for each machine to ensure a safe and productive environment. Both require a commitment to regular care and adherence to safety rules.
How Do the Safety Protocols Differ?
The safety protocols for each machine are very different.
- Laser Engraving: The primary hazards are the high-intensity laser beam and the fumes created during the engraving process.13 The machine must have a fully interlocked enclosure to prevent any exposure to the laser beam. A proper fume extraction and filtration system is absolutely mandatory to remove the fine silica dust and any potential fumes. The complete safety procedure is detailed in how to engrave glass with laser safely.
- CNC Engraving: The primary hazards are the high-speed rotating tool and the wet environment from the coolant. The machine must have a safety enclosure to contain the coolant splash. The operator must never reach into the machine while it is running. The wet floor around the machine can be a slip hazard and requires careful management.
What Does Maintenance Involve for Each Machine?
The maintenance routines for each machine are also distinct.
- Laser Engraver: The key maintenance tasks involve cleaning the laser's optics (lenses and mirrors), cleaning the fume extraction filters, and monitoring the life of the laser tube, which is a consumable item.
- CNC Engraver: The primary tasks involve managing the coolant system, cleaning the machine to prevent the buildup of abrasive slurry, lubricating the mechanical components like guide rails and ball screws, and monitoring the wear of the diamond tools.A full checklist for each is available in our guide on the maintenance of glass engraving machines.
Conclusion
The laser engraving vs CNC engraving for glass decision is a choice between two exceptional technologies, each with its own unique strengths. It is not a question of which is "better," but which is "right" for the specific application. The laser is the master of fine detail, photorealistic imagery, and subtle, frosted elegance.14 The CNC machine is the master of depth, brilliance, and bold, tactile presence. By understanding the fundamental difference between the thermal, non-contact process of the laser and the mechanical, subtractive process of the CNC, a fabricator can confidently select the perfect tool to bring their creative vision to life in the brilliant medium of glass.
